Obesity, a condition often associated with metabolic diseases, has its roots in the fundamental biological functions of body fat. Body fat, or adipose tissue, originally evolved to play a critical role in energy storage, protecting delicate organs, and regulating reproduction through complex hormonal signals. In vertebrates, specialized cells known as adipocytes are responsible for storing energy in the form of lipid droplets. However, despite its important role, excess body fat can lead to severe health issues, including cardiovascular diseases (CVD), and an increased risk of certain cancers and type 2 diabetes (T2D).1 This overview covers the various factors that contribute to obesity as well as the research tools available for studying these pathways.
Key aspects in obesity:
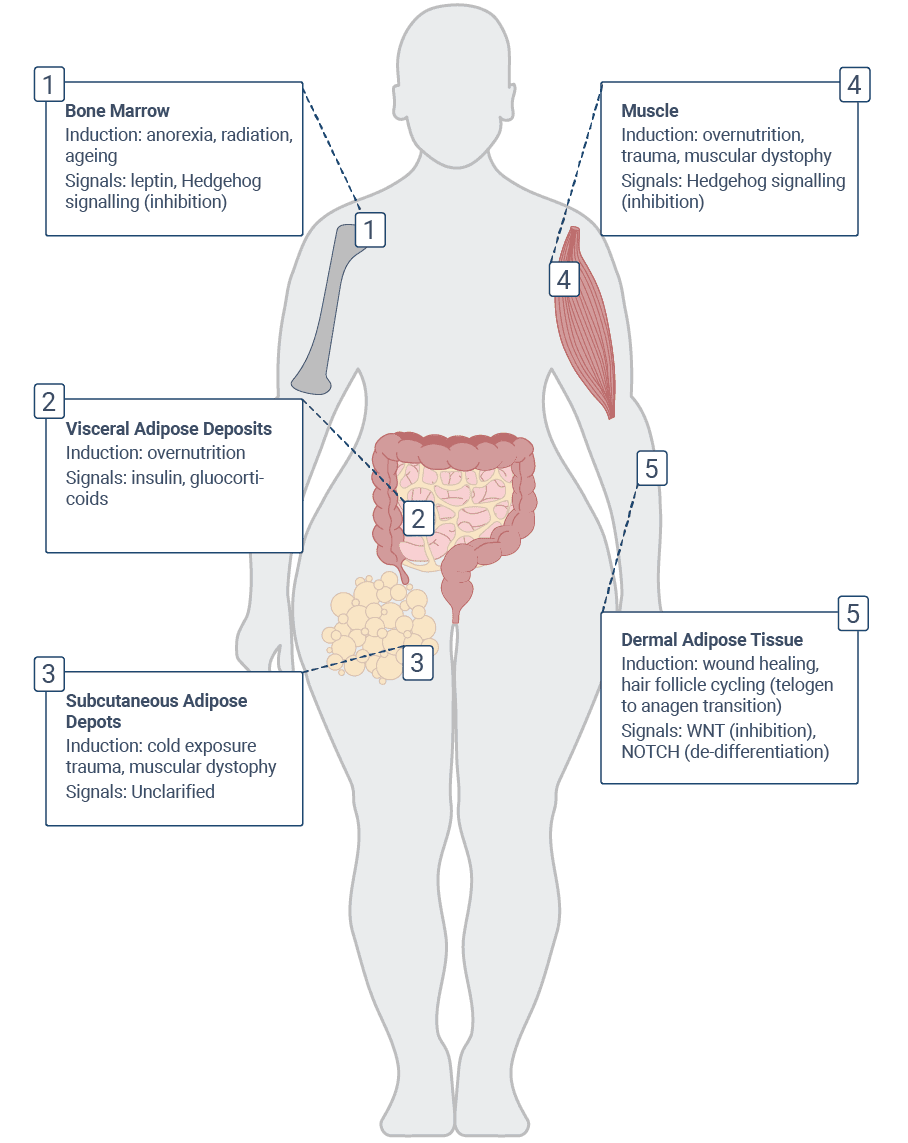
Figure. Sites of adipogenesis in adults (Adapted from Ghaben & Scherer, 2019).
Adipocyte Differentiation and Function
Mammals, including humans, possess three distinct types of adipose tissues: white adipose tissue (WAT), beige (or brite) adipose tissue, and brown adipose tissue (BAT). While all these tissues originate from mesenchymal progenitor cells, the differentiation of adipocytes during adipogenesis is guided by specific proteins and transcriptional factors. Key among these are the transcription factors of the C/EBP family and proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma), with PPARgamma being acknowledged as the primary regulator of adipose tissue biology.2 Additionally, members of the Kruppel-like factor (KLF) family of zinc-finger transcription factors act as both promoters and inhibitors of adipogenesis3, while the tumor suppressor p53 appears to specifically inhibit the formation of white adipocytes.4 The figure above illustrates the various sites of adipogenesis, along with their specific triggers and signaling pathways, emphasizing the complex regulation of adipose tissue differentiation.
Related Products
| Product | Type | Reactivity | Applications |
| KLF4 Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse | WB, ELISA, IF |
| KLF4 Antibody [4G6E11] | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA |
| KLF4 Antibody [4E5C3] | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA |
| p53 Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, IF, Multiplex |
| p53 phospho S392 Antibody | Antibody | Rat | WB |
| p53 K292 Ac Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, Dot Blot |
| p53 K305 Ac Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, Dot Blot |
| Human P53 ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| PPAR gamma 1 + 2 Antibody | Antibody | Broad | WB, ELISA |
| PPAR gamma phospho pS273 Antibody | Antibody | Human | ELISA, Dot Blot |
| PPAR gamma 2 Antibody | Antibody | Mouse | WB, ELISA, IHC |
Adipokines
Adipokines are a set of cytokines that are produced and secreted by adipocytes or immune cells infiltrating the adipose tissue. They act as paracrine and endocrine factors, influencing energy expenditure, metabolic balance, inflammatory and immune responses, cardiovascular health, and various other physiological functions. Adipokine profiles are specifically characterized by a reduction in anti-inflammatory adipokines (such as adiponectin) and an increase in pro-inflammatory adipokines (such as leptin, resistin, and NAMPT). Changes in adipokine profiles are believed to be pivotal in the development and progression of obesity.5
Further reading:
Related Products
| Product | Type | Reactivity | Applications |
| Adiponectin Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC |
| Adiponectin Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
| Leptin Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse | WB, ELISA |
| Leptin Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse | WB, ELISA |
| Human Progranulin ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse Progranulin ELISA Kit | Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Human RBP4 ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse RBP4 ELISA Kit | Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| rHuman Resistin Dimer Protein | Protein | Human | SDS-PAGE, Cellular Assay |
| rHuman Visfatin Protein | Protein | Human | SDS-PAGE, Cellular Assay |
| Human Resistin ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Components
The extracellular matrix (ECM) plays a crucial role in adipose tissue, providing structural support to adipocytes, protecting them from mechanical stress, and acting as a reservoir for growth factors and cytokines. In adipose tissue, the ECM primarily consists of collagens (types I, II, III, and IV), fibronectin, and a small amount of laminin.6 Remodeling of healthy adipose tissue involves the continuous turnover of ECM proteins through a cycle of matrix deposition and degradation, primarily mediated by enzymes such as metalloproteinases (MMPs).7 These MMPs are regulated by specific endogenous inhibitors, like tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs). The balance between activated MMPs and TIMPs determines the overall activity of MMPs, and an imbalance is often observed in obese adipose tissues.6
Further reading:
Related Products
| Product | Type | Reactivity | Applications |
| Collagen Type I Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Pig | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF, FC, Dot Blot, IP, Multiplex |
| Collagen I alpha 1 propeptide Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
| Collagen I alpha 1 telopeptide Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat, Sheep | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
| Collagen Type II Antibody | Antibody | Human, Bovine | IHC, IF, Dot Blot, Multiplex |
| Collagen Type III Antibody | Antibody | Human, Bovine, Pig | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF, FC, Dot Blot, Multiplex |
| Collagen Type IV Antibody | Antibody | Human, Bovine | WB, IHC, IF, Dot Blot, Multiplex |
| Collagen Type IV Antibody | Antibody | Mouse | ELISA, IHC, IF |
| Bovine Collagen Type I | Protein | Bovine | WB, SDS-PAGE |
| Human Collagen Type I | Protein | Human | WB, SDS-PAGE, Cellular |
| Bovine Collagen Type II | Protein | Bovine | SDS-PAGE |
| Human Collagen Type II | Protein | Human | WB, SDS-PAGE |
| Bovine Collagen Type III | Protein | Bovine | SDS-PAGE |
| Human Collagen Type III | Protein | Human | WB, SDS-PAGE |
| Bovine Collagen Type IV | Protein | Bovine | SDS-PAGE |
| Human Collagen Type IV | Protein | Human | ELISA, SDS-PAGE |
| Fibronectin Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, IHC, IF |
| Human Fibronectin ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse Fibronectin ELISA Kit | Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Rat Fibronectin ELISA Kit | Kit | Rat | ELISA |
| Laminin Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, ELISA, IHC, Other |
| Human Laminin ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse Laminin ELISA Kit | Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Rat Laminin ELISA Kit | Kit | Rat | ELISA |
| Human MMP-1 ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| MMP2 Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
| Human MMP-2 ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse MMP-2 ELISA Kit | Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Rat MMP-2 ELISA Kit | Kit | Rat | ELISA |
| Human MMP-3 ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse MMP-3 ELISA Kit | Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Mouse MMP-9 ELISA Kit | Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| TIMP1 Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, IHC |
| Human TIMP-1 ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse TIMP-1 ELISA Kit | Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Rat TIMP-1 ELISA Kit | Kit | Rat | ELISA |
| Human TIMP-2 ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse TIMP-2 ELISA Kit | Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Rat TIMP-2 ELISA Kit | Kit | Rat | ELISA |
| Human TIMP-3 ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
Fibrosis Markers
Fibrosis is one of the hallmarks of obese adipose tissue, marked by excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) and increased collagen alignment. The platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) pathway plays a central role in regulating fibroblast activation and promotes the de-differentiation of adipocytes into fibroblasts/myofibroblasts. This process is associated with increased expression of fibrotic markers, including collagen I, collagen VI, alpha-smooth muscle actin (ASMA), and fibroblast-specific protein 1 (FSP1). The involvement of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) pathway in tissue fibrosis is also well-established. When TGF-beta binds to its receptors, TGF-beta receptor 1 (TGFBR1) and TGF-beta receptor 2 (TGFBR2), it activates the canonical SMAD2/3 pathway, leading to the expression of various ECM-related genes.8
Related Products
| Product | Type | Reactivity | Applications |
| Collagen Type VI Antibody | Antibody | Human, Bovine | IHC, IF, Dot Blot, Multiplex |
| Human Collagen Type VI | Protein | Human | IF, SDS-PAGE, Cellular Assay |
| Bovine Collagen Type VI | Protein | Bovine | - |
| rHuman PDGF-AA Protein | Protein | Human | SDS-PAGE, Cellular Assay |
| rMouse PDGF-AA Protein | Protein | Mouse | SDS-PAGE, Cellular Assay |
| rHuman PDGF-AB Protein | Protein | Human | SDS-PAGE, Cellular Assay |
| Human PDGF-AB ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse PDGF-AB ELISA Kit | Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Rat PDGF-AB ELISA Kit | Kit | Rat | ELISA |
| rHuman PDGF-BB Protein | Protein | Human | SDS-PAGE, Cellular Assay |
| rMouse PDGF-BB Protein | Protein | Mouse | Cellular Assay |
| PDGF-B Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IF |
| TGF beta 1 Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, ELISA, IHC |
| rHuman TGF beta 1 Protein | Protein | Human | Cellular Assay |
| Human TGF beta 1 ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse TGF beta 1 ELISA Kit | Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Rat TGF beta 1 ELISA Kit | Kit | Rat | ELISA |
| Human TGF beta 2 ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse TGF beta 2 ELISA Kit | Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Rat TGF beta 2 ELISA Kit | Kit | Rat | ELISA |
| Human TGF beta 3 ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse TGF beta 3 ELISA Kit | Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Rat TGF beta 3 ELISA Kit | Kit | Rat | ELISA |
Glucose Metabolism
Glycolysis is a specific pathway within glucose metabolism and describes the energy-producing process where one glucose molecule is broken down into two pyruvate molecules. When oxygen is available, pyruvate typically moves into the mitochondria and is converted to acetyl-CoA as part of the TCA cycle. Without oxygen, pyruvate is transformed into lactate. Glycolysis consists of 10 steps occurring in the cytosol, producing two ATP molecules without needing oxygen. Three main regulatory steps in glycolysis, carried out by hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase, are crucial for ensuring the process flows towards pyruvate and are effectively irreversible. Dysregulation and excessive glucose availability and the subsequent increase in glycolytic flux can lead to enhanced fat storage and insulin resistance, both hallmarks of obesity.9
Related Products
| Product | Type | Reactivity | Applications |
| Aldolase Antibody | Antibody | Human, Rabbit | WB, IP |
| Aldolase Antibody | Antibody | Human, Rabbit | WB, ELISA, IP |
| Fructose-6-Phosphate Kinase Antibody | Antibody | Rabbit | WB, ELISA, IF, Multiplex |
| Fructose-6-Phosphate Kinase Antibody | Antibody | Rabbit | WB |
| GAPDH Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rabbit | WB, ELISA, Multiplex |
| GAPDH Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC |
| GAPDH Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA |
| GAPDH Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse | WB, ELISA |
| Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Antibody | Antibody | Leuconostoc mesenteroides | WB |
| Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Antibody | Antibody | Leuconostoc mesenteroides | - |
| Hexokinase Antibody | Antibody | Hexokinase (Yeast) | WB, ELISA |
| Hexokinase Antibody | Antibody | Hexokinase (Yeast) | WB |
| Lactate Dehydrogenase Antibody | Antibody | Human, Rabbit | WB, ELISA, IF, Other |
| Lactate Dehydrogenase Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, ELISA |
| Neuron specific enolase (NSE) Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Chicken | WB, IHC, IF, Multiplex |
| Pyruvate Kinase Antibody | Antibody | Rabbit | WB |
| Pyruvate Kinase Antibody | Antibody | Rabbit | - |
| PKM2 Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB |
Glucose Transporters
A family of facilitative glucose transporters (GLUTs) play a critical role in regulating glucose uptake within adipose tissue. Growing evidence strongly supports the involvement of various GLUT family members in the development and progression of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes (T2D). Among these transporters, GLUT4 is the most prevalent isoform in adipocytes and is primarily responsible for insulin-stimulated glucose uptake, with its expression significantly downregulated in T2D. GLUT1 contributes to basal glucose transport and undergoes recycling through internal membrane compartments, while GLUT8 expression increases during fat cell differentiation, suggesting a potential role in embryonic tissue development.10
Related Products
| Product | Type | Reactivity | Applications |
| Glut2 Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
| Glut2 Antibody | Antibody | Mouse | WB, ELISA |
Gut Microbiota-Related Targets
The gut acts as the main habitat for a diverse and abundant collection of microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, protists, and algae, collectively known as the gut microbiota. Chronic, low-grade systemic inflammation is widely recognized as a hallmark of metabolic diseases and is largely attributed to elevated levels of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in the bloodstream. Individuals with obesity often experience gut microbiota imbalances, characterized by an overabundance of LPS-producing gram-negative bacteria. This increase in LPS can directly activate the TLR4/MyD88/IRAK4 signaling pathway in intestinal mucosal epithelial cells, leading to increased intestinal permeability. The disruption of tight junction integrity is believed to be a potential driver of inflammation in obesity.11
Hormones and Metabolic Regulators
Gut hormones are crucial regulators of metabolism, orchestrating the body's response to food intake by influencing appetite, energy expenditure, and glucose homeostasis. Among these hormones, incretins, particularly glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), have gained significant attention not only for their role in enhancing insulin secretion in response to food intake but also for their impact on body weight. Originally studied for their anti-diabetic properties, GLP-1 and its analogs were found to induce weight loss through mechanisms that include reducing appetite and slowing gastric emptying. Similarly, amylin, another hormone co-secreted with insulin by pancreatic beta cells, has been observed to contribute to weight regulation by promoting satiety and inhibiting food intake. Ghrelin, known as the "hunger hormone", is the most proximally located hormone that influences appetite. Beyond these hormones, other metabolic regulators also contribute to the pathophysiology of obesity.12
Further reading:
Related Products
| Product | Type | Reactivity | Applications |
| GDF15 Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, ELISA |
| GDF15 Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse | WB, ELISA |
| GDF15 Antibody | Antibody | Human | ELISA |
| GDF15 Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, ELISA |
| GDF15 Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, ELISA |
| GDF15 Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, ELISA |
| GDF15 Antibody | Antibody | Human | ELISA |
| GDF15 Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse | WB, ELISA, IHC |
| GDF15 Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse | WB, ELISA |
| GDF15 Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse | WB, ELISA |
| GDF15 Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse | WB, ELISA |
| rHuman GDF15 Protein | Protein | Human | SDS-PAGE |
| rHuman GDF15 (D variant) Protein | Protein | Human | SDS-PAGE |
| Human GDF15 ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse GDF15 ELISA Kit | Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| GLP-1 (7-36, amide) | Protein | Human | - |
| Glucagon Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
| Glucagon Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit | IHC |
| Insulin Antibody | Antibody | Human | ELISA, Dot Blot |
| UCP1 Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC |
Inflammatory Markers
Obesity is a multifaceted condition linked to elevated levels of various inflammatory markers, resulting in persistent low-grade inflammation. Overweight and obese individuals exhibit modified serum concentrations of inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), C-reactive protein (CRP), and interleukins (IL-6, IL-18). These pro-inflammatory agents are crucial in the development of insulin resistance and the heightened risk of cardiovascular diseases seen in obesity. It is proposed that visceral fat contributes to systemic inflammation by directly releasing free fatty acids and inflammatory cytokines into the portal circulation.13
Further reading:
Related Products
| Product | Type | Reactivity | Applications |
| CRP Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, Dot Blot |
| CRP Antibody | Atnibody | Human | - |
| Human CRP ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse CRP ELISA Kit | Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Rat CRP ELISA Kit | Kit | Rat | ELISA |
| IL-6 Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, IHC, Dot Blot |
| IL-6 Antibody | Antibody | Mouse | WB, IHC, FC |
| IL-6 Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, IHC |
| IL-6 Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, ELISA, FC, Multiplex |
| rHuman IL-6 Protein | Protein | Human | SDS-PAGE |
| rHuman IL-6 Protein | Protein | Human | SDS-PAGE |
| rMouse IL-6 Protein | Protein | Mouse | WB, IHC, SDS-PAGE |
| rRat IL-6 Protein | Protein | Rat | Cellular Assay |
| rRat IL-6 Protein | Protein | Rat | - |
| Human IL-6 ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse IL-6 ELISA Kit | Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Rat IL-6 ELISA Kit | Kit | Rat | ELISA |
| IL-18 Antibody | Antibody | Mouse | WB, IHC, IF |
| Human IL-18 ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Rat IL-18 ELISA Kit | Kit | Rat | ELISA |
| TNF alpha Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, IHC, IF |
| TNF alpha Antibody | Antibody | Human, Primate | WB, IHC, IF |
| TNF alpha Antibody | Antibody | Mouse | WB, IHC |
| TNF alpha Antibody | Antibody | Mouse | WB |
| TNF alpha Antibody | Antibody | Pig | WB |
| Recombinant Anti-TNF alpha Fab Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, ELISA |
| rHuman TNF alpha Protein | Protein | Human | SDS-PAGE, Cellular Assay |
| rHuman TNF alpha Protein | Protein | Human | SDS-PAGE |
| rMouse TNF alpha Protein | Protein | Mouse | SDS-PAGE, Cellular Assay |
| rRat TNF alpha Protein | Protein | Rat | SDS-PAGE |
| Human TNF alpha ELISA Kit | Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse TNF alpha ELISA Kit | Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Rat TNF alpha ELISA Kit | Kit | Rat | ELISA |
Lipid Metabolism Enzymes
Lipid metabolism is a fundamental process in energy homeostasis, involving the breakdown and storage of fatty acids. ATGL is the initial enzyme responsible for the hydrolysis of triglycerides (TG) within adipocytes. LIPE, also known as hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL), is responsible for the second step of lipolysis resulting and hydrolyzes diacylglycerols (DAG) into monoacylglycerols (MAG) and free fatty acids.14 LPL is another critical enzyme in lipid metabolism, primarily responsible for the hydrolysis of triglycerides in circulating lipoproteins. LPL is anchored to the endothelial surface of capillaries in tissues, where it acts at the interface between the bloodstream and tissue cells.15
Related Products
| Product | Type | Reactivity | Applications |
| LIPE Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
Oxidative Stress Markers
Oxidative stress plays a crucial role in the pathophysiology of obesity, driving the development of various metabolic complications. In conditions such as obesity, insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, chronic inflammation, and dyslipidemia, overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) can occur. The excessive ROS generated in these pathological states can cause significant cellular damage, including DNA damage and lipid peroxidation. NADPH Oxidase 4 (NOX4) is a major source of ROS production, and its expression is frequently upregulated in adipose tissue, further amplifying oxidative stress and tissue damage. Counteracting this, the superoxide dismutase (SOD) family, comprising SOD1, SOD2, and SOD3, plays a vital role in mitigating oxidative stress by catalyzing the conversion of superoxide radicals into less harmful molecules like hydrogen peroxide.16
Related Products
| Product | Type | Reactivity | Applications |
| FTO Antibody | Antibody | Human | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
| FTO Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB |
| NOX4 Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
| SOD1 Antibody | Antibody | Broad | WB, IHC, IP |
| SOD1 Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | WB, IHC, IF, IP |
| SOD2 Antibody | Antibody | Broad | WB, IHC, IP |
| SOD2 Antibody | Antibody | Broad | WB, IHC, IF, IP |
| SOD3 Antibody | Antibody | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IF |
Signaling Pathways
The "bone-fat switch" is a key concept where pathways like Wnt and hedgehog promote osteogenesis while inhibiting adipogenesis in precursor cells. Wnt signaling suppresses adipogenesis by activating β-catenin, favoring bone formation over fat development. The hedgehog pathway similarly inhibits fat cell formation while encouraging bone growth. TGF-β/BMP signaling plays a dual role, where TGF-β inhibits and BMP4 promotes adipogenesis, influencing the balance between fat and bone cell differentiation. Notch signaling, known for its complex effects, can both promote early adipocyte differentiation and inhibit it through repression of PPARgamma. The MAPK pathway, through ERK1 and p38, regulates adipocyte proliferation and differentiation phases, impacting fat tissue expansion. The Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) pathway, particularly through FGFs like FGF1 and FGF10, promotes adipogenesis and plays a role in energy metabolism, linking it to obesity.17
Further reading: