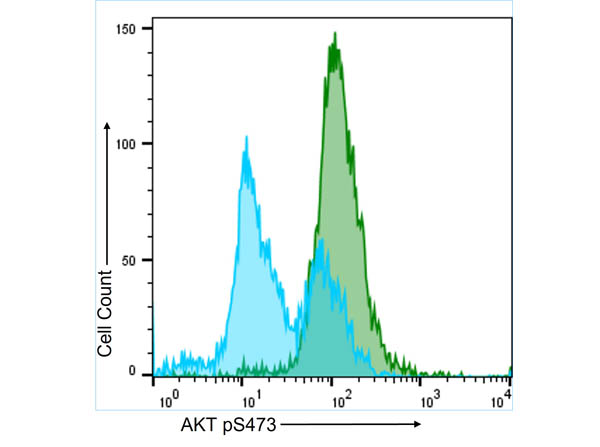
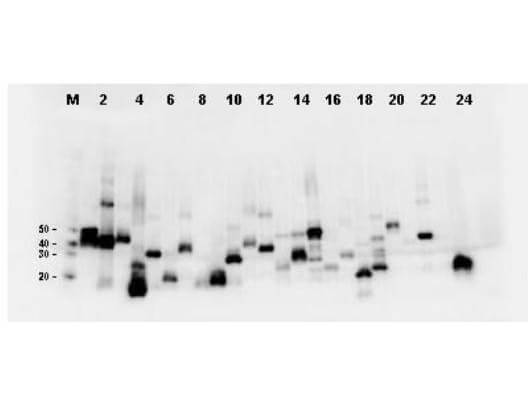
Monoclonal Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies are indispensable tools in scientific research, diagnostics, and therapeutic applications, derived from a single unique parent cell for unparalleled specificity. This category encompasses antibodies produced through the fusion of myeloma cells with spleen cells from an immunized host, creating hybridomas that generate antibodies targeting a single epitope. Their high specificity minimizes cross-reactivity and background noise, providing clear and precise results in various applications:
- High specificity: Target a single epitope, ensuring precise antigen detection
- Low cross-reactivity: Minimize non-specific binding for cleaner results
- Consistent performance: Derived from a single cell line for uniformity across experiments
Product Categories
Applications
Reactivity
Host Species
Conjugation
Format
Post-Translational Modification
Sample Size