Sandwich ELISA Protocol for Collagen
- 11 steps
- 3 days
- 8 reagents required
Because Rockland collagen antibodies are designed with specificity to recognize only non-denatured three-dimensional epitopes, assays that maintain native collagen structure work best. For ELISA, Sandwich ELISA is recommended. A “titering” ELISA, on the other hand, is not recommended because the native collagen structure is disrupted when collagen is directly bound to the ELISA plate. As a result, loss of detection specificity may occur due to: (1) incomplete binding to the plate for some collagen types, (2) partial denaturation of some collagens, and/or (3) partial or incomplete blocking.
This protocol accounts for the design and function of collagen antibodies to optimize the specificity of the antibody. Deviations from the protocol are encouraged but may require additional optimization by the end user to preserve antibody specificity.
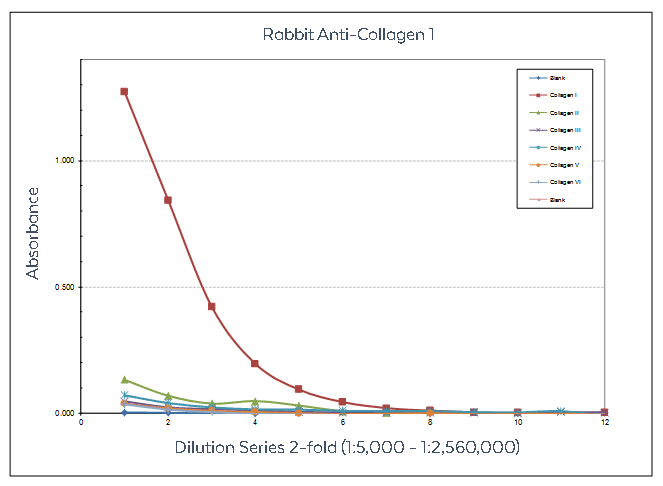
Figure: Sandwich ELISA using Rockland collagen antibodies designed to recognize non-denatured three-dimensional epitopes present within native collagen structure. Anti-Collagen Type I was used to capture Human Collagen Type I and other human collagens. Detection occurred using anti-Collagen Type I Biotin Conjugate followed by reaction with streptavidin HRP and TMB substrate.
Reagents Required
| Product | Preparation |
| 96-Well Clear Flat Bottom PVC Plates | We recommend Corning® Costar™ 96-well clear flat bottom PVC general assay plates #2595 |
| Capture Antibody | For capture of Collagen Type I, use Anti-Collagen Type I |
| Collagen Analytes | For capture of Collagen Type I, use Human Collagen Type I |
| Detection Antibody | For detection of Collagen Type I, use Anti-Collagen Type I Biotin Conjugate |
| Detection Reagents | Use Streptavidin Peroxidase Conjugate and TMB ELISA Peroxidase Substrate |
| Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) |
Procedure
-
Coat plate with 100 µL of capture antibody diluted to 10 µg/mL in Borate Buffered Saline (BBS) pH 8.5. Allow binding to occur overnight at room temperature.
-
Add blocking reagents to block plates by adding 200 µL of 1% BSA, 0.1% Tween-20 in BBS to each well. Allow blocking to occur overnight at room temperature.
-
Wash plates three times with BBS supplemented with 0.1% Tween-20.
-
Add 100 µL of collagen analyte in BBS supplemented with 0.1% Tween-20 and 0.05% SDS at 0.5 µg/mL. Allow binding to occur overnight at room temperature.
-
Wash plates three times with BBS supplemented with 0.1% Tween-20.
-
Add 100 µL of BBS to all wells except controls in preparation for serial dilution of detection antibody.
-
Add 100 µL of detection antibody diluted to 1:2,500 in BBS from a 1 mg/mL stock to the first well. Mix resulting in a 1:5,000 dilution. Perform serial two-fold dilutions across the plate. Allow binding to occur overnight at room temperature.
-
Wash plates three times with BBS supplemented with 0.1% Tween-20.
-
Add 100 µL of detection reagent Streptavidin-HRP diluted from a 1 mg/mL stock to 1:5,000 in BBS.
-
Wash plates three times with BBS supplemented with 0.1% Tween-20.
-
Add 100 µL TMBE substrate. Allow color to develop. Scan the plate to determine absorbance values.